Hashgraph vs Blockchain: Hedera Hashgraph Explained
Imagine you are launching a new digital service: you need to quickly verify the authenticity of customer documents, securely store data, and automate settlements with partners in different countries. An error in these processes can cost a company millions, and a slow system will drive customers away.
That is why business owners are increasingly turning their attention to Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT).
According to Statista, the global DLT market will exceed $127 billion by 2030 — an increase of more than $100 billion compared to 2020. The main driver is supply chain audits, which will reach $103 billion by the end of the decade, but other areas are also actively developing: digital identity, smart contracts, and immutable records.
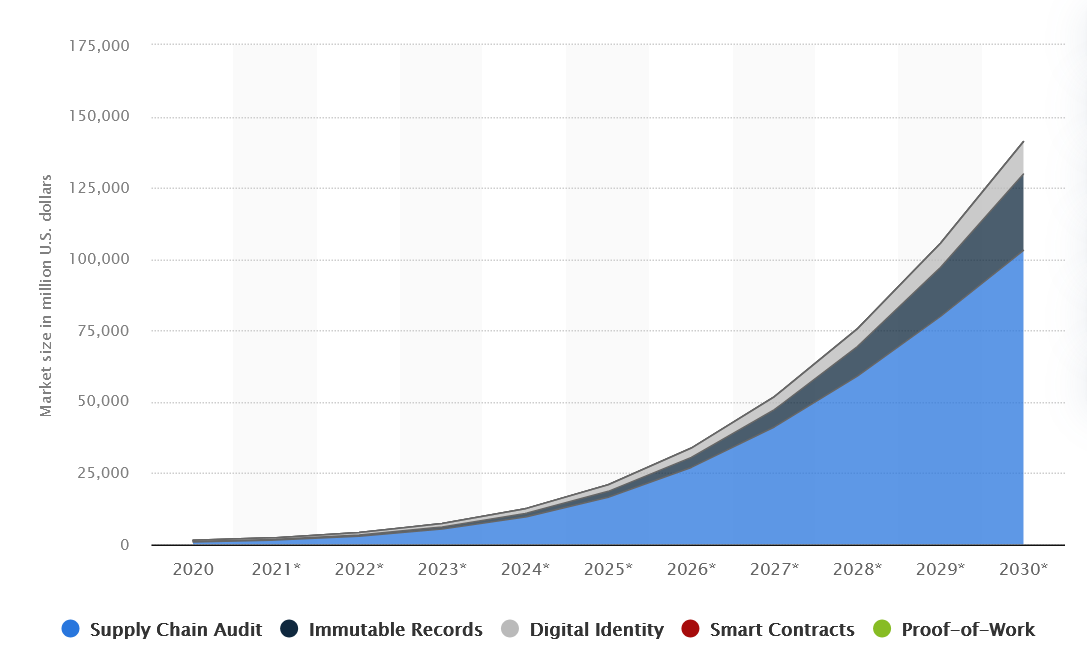
Distributed ledger market size worldwide from 2020 to 2030
Amid this rapid expansion, the question of “hashgraph vs blockchain” has become a key consideration for businesses and developers exploring distributed ledger technologies.
On the one hand, blockchain has become the foundation for projects such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, proving that decentralization can successfully work in real business.
On the other hand, hashgraph offers a different path: higher transaction speed, energy-efficient consensus, and new opportunities for enterprise solutions.
For companies, this is no longer a question of “technology for technology’s sake.” It is a strategic choice: on which platform to build digital products and business services in order to remain competitive tomorrow.
Fundamentals of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT)
Today, many companies are considering implementing digital solutions where trust in data plays a key role.

Imagine a situation: several partners from different countries are working on one project, and each of them needs to be sure that the records of transactions or documents are accurate and cannot be tampered with.
In traditional systems, this trust is provided by a single central authority — a bank, a government agency, or a service provider. But what if there is no center?
Distributed ledger technologies step in here, serving as the backbone for innovations like blockchain and hashgraph, and increasingly becoming a topic of active discussion in the business world.
What Is DLT?
Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) are a way of simultaneously storing and synchronizing data across all participants in a network. Instead of relying on a single server, information is copied and updated across multiple nodes at the same time.
The key difference is simple. A centralized system depends on one operator. If that operator goes down, everyone feels the impact. With DLT, the data is spread out, so every participant sees the same version of events. This makes the system more transparent and much harder to break.
Thanks to this, companies can build services where participants trust the data without having to trust each other directly.
The first real-world applications of distributed ledgers were made possible by the advent of blockchain, which first gained attention through cryptocurrencies. In 2009, Bitcoin showed that value could be exchanged directly between individuals without relying on banks or intermediaries.
A few years later, Ethereum expanded the concept of blockchain by introducing smart contracts — self-executing programs that automatically carry out agreements. These innovations pushed blockchain far beyond the crypto community and paved the way for a wide range of business applications.

Hashgraph as a New Type of DLT
If blockchain was the first mass form of DLT, then hashgraph technology is positioned as its development.
Unlike a linear chain of blocks, hashgraph uses the structure of a directed acyclic graph (DAG), where transactions are recorded not one by one, but in parallel. This allows processing thousands of transactions per second with minimal costs.
The main differences from traditional blockchain are:
- Speed — hashgraph can handle up to 10,000 transactions per second, while Bitcoin is limited to about 7 and Ethereum to around 30 (these numbers are for public blockchains; private ones can process up to 2,000 transactions per second).
- Energy efficiency — thanks to the virtual voting mechanism and gossip protocol, the network does not require resource-intensive computations like PoW.
- Transaction finality — confirmations occur instantly, without the need to wait for multiple blocks.
Differences Between Hashgraph and Blockchain
To understand the differences between blockchain and hashgraph, it is important to analyze how they work. At first glance, both technologies fall under DLT and solve a similar problem — storing and verifying data in a decentralized network. However, their mechanisms and architecture differ significantly.
How Does Blockchain Work?
In blockchain, data is grouped into blocks that are connected into a chain. Each new block is linked to the previous one, and changing an old record without altering the entire chain is practically impossible.
The network is maintained by nodes (computers) that validate transactions and store identical copies of the database. Blockchain also supports smart contracts — small programs that automatically execute the terms of an agreement.
To decide which transactions are valid, the network uses a consensus mechanism. The most popular options are:
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) — used in Bitcoin, where miners solve puzzles to add a block (reliable, but very energy-intensive).
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) — for example, in Ethereum: new blocks are validated by participants who have staked their cryptocurrency. This method is faster and more resource-efficient.
How Does Hashgraph Work?
Hashgraph works differently. There is no chain of blocks. As we stated above, it uses a structure called a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), where transactions are recorded in parallel rather than one by one, which gives the network greater speed.
Information in hashgraph spreads through the gossip-about-gossip method: each node shares what it knows with others, and in this way, data quickly propagates across the entire network.
On this basis, virtual voting is used: nodes do not need to vote; they can simply calculate the result, since they all have the same information. This is the hashgraph consensus — a fast, fair, and secure way to agree on the validity of transactions.
Hashgraph vs Blockchain: Detailed Comparison
For businesses, choosing the right blockchain network or alternative DLT like Hedera Hashgraph is a strategic decision.
We have already looked at how blockchain and hashgraph work, but for businesses, it is important to see the clear differences in figures and characteristics. The table below provides a side-by-side comparison of both technologies across key parameters — from architecture to performance.
Criterion
Blockchain
Hashgraph (Hedera)
Architecture
Linear chain of blocks. Each transaction is added sequentially.
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). Transactions are recorded in parallel.
Throughput
Limited: Bitcoin ~7 TPS, Ethereum ~30 TPS (for public blockchains).
High: up to 10,000+ TPS in the Hedera Hashgraph network.
Transaction cost
Can be high under load: from a few cents to tens of dollars (for public blockchains).
Very low: fractions of a cent per transaction.
Consensus algorithm
Proof-of-Work (energy-intensive) or Proof-of-Stake (less costly but complex to manage).
Hashgraph consensus based on gossip-about-gossip and virtual voting.
Energy efficiency
Low in PoW (huge mining costs), higher in PoS.
Very high: no heavy computations, only information exchange.
Security
Vulnerable to 51% attack: an attacker with majority power can rewrite history.
Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (ABFT). The network remains honest even if some nodes fail.
Finality
Requires waiting for several blocks (in public blockchains): in Bitcoin — up to 60 minutes.
Instant finality — transactions are confirmed right away.
Scalability
Limited: higher load = higher fees and slower confirmations.
High: designed for enterprise-level performance.
Use cases
Bitcoin, Ethereum, DeFi, NFT, supply chain (business-specific solutions for private blockchains are available).
Hedera Hashgraph: micropayments, digital identity, enterprise applications.
Hashgraph vs Blockchain
Overview of Hedera Hashgraph
When people talk about hashgraph, they usually mean its most well-known implementation — the Hedera Hashgraph platform. This network became one of the first practical attempts to turn DAG technology and hashgraph consensus into a working ecosystem available to companies and users worldwide.
What Is the Hedera Hashgraph Platform?
Hedera Hashgraph is a public network designed to give businesses and developers a fast, secure, and scalable way to use distributed ledgers. Unlike many blockchains, Hedera is not built around cryptocurrency as its core value. Instead, it provides a platform for creating applications — from micropayments to digital identity systems.
Key features:
- High performance: thousands of transactions per second with low fees.
- Transparency and trust: all participants have equal access to data.
- Energy efficiency: no costly mining, unlike blockchain.
The network is governed by the Hedera Governing Council — a board that includes major global companies (Google, IBM, Boeing, and others). This approach builds trust with businesses, since decisions are made not by a single operator but by a group of independent participants.
Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain: Competition or Coexistence?
Many companies wonder whether Hedera Hashgraph can replace existing blockchain solutions or at least integrate with them. In practice, it is more about coexistence than competition.
Hedera does not set itself against blockchain but rather complements the DLT ecosystem. It can be used as a standalone platform or alongside other technologies. For example, hashgraph is ideal for micropayments, high-throughput applications, or IoT, while blockchain retains its strong position in cryptocurrencies, DeFi, and NFTs thanks to its mature infrastructure and broad ecosystem.
In terms of strengths:
- Hashgraph wins where speed, scalability, low transaction cost, and instant finality are essential.
- Blockchain remains indispensable where market trust and ecosystem maturity matter most — cryptocurrencies, DeFi, NFTs, and large-scale public projects.
Thus, in the coming years, businesses should focus not on choosing “either-or” but on hybrid architectures where blockchain and hashgraph are applied together, depending on the task.
Future of DLT: Can Hashgraph Replace Blockchain?
Today, it is difficult to name a clear winner in the debate between blockchain and hashgraph. On the one hand, blockchain has already proven its value: it has become the foundation for the largest cryptocurrencies, thousands of projects are built on it, and investors continue to pour billions into its ecosystem.
On the other hand, hashgraph is gradually attracting market attention, especially through the Hedera Hashgraph network, which is supported by leading global corporations. Its speed, energy efficiency, and reliable consensus make the technology appealing for enterprise solutions.
According to analysts, the DLT market will grow to hundreds of billions of dollars by 2030, and both blockchain and hashgraph will share in this growth. It is unlikely that one technology will completely replace the other.

SCAND and Distributed Ledger Technologies Development
At SCAND, we have extensive experience in developing solutions based on blockchain technologies — from smart contracts and crypto wallets to decentralized applications (DAO, DeFi, NFT, and Web3). We help companies leverage distributed ledgers to improve transparency, security, and automation of business processes.
Lately, we have been actively exploring the potential of the Hedera Hashgraph network. This technology opens new opportunities for enterprise solutions thanks to its high transaction speed, energy efficiency, and instant finality.
Why choose us:
- We have deep expertise in smart contract development, blockchain development, and work with various DLT platforms.
- We deliver custom solutions tailored to specific business needs — whether it’s payment systems, digital identity, supply chain management, or micropayments.
We see ourselves not just as developers but as a partner who helps integrate modern DLT solutions and unlock their potential for business growth and competitiveness.



