6 Ways To Fix the 400 Bad Request Error

You’ve just launched a new promotion on your online store, and customers are flocking to your website. Everything seems to go smoothly until you try to access the product page for one of your bestsellers — and lo and behold — you’re met with a message that strikes fear in the hearts of business owners: “400 Bad Request.”
Panic sets in. What does this mean? How many customers are seeing this error instead of your products? How is this affecting your business?
If you’ve ever felt the frustration of getting an error instead of the webpage you expected, or woken up in a cold sweat imagining it happening on your site at a critical moment — you’re not alone. The 400 Bad Request error can be a thorn in the side of entrepreneurs and small business owners who rely on their websites for success.
But don’t worry.
This guide is here to help you understand and fix this issue so you can return to providing a seamless experience for your customers.
Why Understanding HTTP Errors Matters for Your Business
Your website is often the first point of contact between you and potential customers. HTTP errors like the 400 Bad Request can disrupt this connection, leading to a poor user experience, lost sales, and even a dent in your search engine rankings.
For small businesses and entrepreneurs, every visitor counts, and making sure your website runs smoothly is how you keep growing, maintain your reputation, and run a successful online business.
Understanding and promptly resolving errors isn’t just about fixing a technical glitch — it’s also about maintaining professionalism, building trust with your audience, and protecting the online presence you’ve worked so hard to establish.
What Is the 400 Bad Request Error?
When you or any site’s visitors try to access a page, your browser sends a request to the website’s server. The server then processes the request and returns the desired information — unless something goes wrong. The 400 Bad Request error is an HTTP status code that indicates the server couldn’t understand the request because of invalid syntax.
In simpler terms, the server thinks there’s something wrong with the client’s request. Instead of loading the page, it displays an error message, leaving both you and your visitors in the dark.
Variations of the Error Message
While this error typically shows up as “400 Bad Request,” it can manifest in several ways, so you may see some variations:
- “Bad Request – Invalid URL”
- “HTTP Error 400”
- “Bad Request. Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand.”
- “HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request”
- “HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request”
- “400 – Bad Request. The request could not be understood by the server due to malformed syntax. The client should not repeat the request without modifications.”
- “400 Bad Request. Request Header Or Cookie Too Large”
- “Bad Request – Error 400”
Regardless of how it’s phrased, the message indicates the same issue: the server can’t process the request because of a client-side error. The 400 Bad Request error can be very frustrating, as it blocks access to the site without giving you any helpful information.
Let’s discuss some of the most common causes.
Common Causes of the 400 Bad Request Error
When a server returns a 400 Bad Request, it means that it can’t understand and process your request. Usually, this is because of a client-side error, which means there’s a problem at your end.
Understanding what triggers this error is the first step toward fixing it. Here are some common issues that may cause a 400 Bad Request error:
- Invalid URL syntax: You may have mistyped the URL or used invalid characters. This can include typos, misplaced characters, or unsupported symbols in the URL.
- Corrupted browser cache or cookies: Outdated or corrupt files stored by your browser can interfere with requests. If your browser cookies have expired or your cache is corrupted, the server may not be able to process your request properly.
- Conflicting browser extensions: In some cases, your browser extensions can interfere with the request and cause a 400 Bad Request. Add-ons or extensions might block or alter requests unintentionally.
- Bad DNS cache: Outdated DNS information can lead to miscommunication with the server. Your locally cached DNS data could be out of sync with the current DNS registration for the domain.
- Large uploaded file size: Attempting to upload files that exceed the server’s size limits can cause an error. If you’re uploading a large file to a site, it could exceed the maximum upload limit and therefore, cause the error.
- Server-side issues: Misconfigured server settings or temporary glitches could also cause a 400 Bad Request error. For example, the website may have a misconfigured server or a temporary glitch. While less usual, don’t write it off.
How To Fix the 400 Bad Request Error (6 Methods)
Now that we’ve pinpointed potential causes, let’s dive into actionable solutions to get your website back on track.
When you first see a 400 Bad Request error, try refreshing the page. Sometimes, this will resolve any temporary glitches. If it doesn’t work, you can try the following steps.
1. Check for Errors in the Address
Check your URL for any errors. This is one of the most common causes of a 400 Bad Request. There could be typos, malformed syntax, or extra characters in the address.
Why this helps: A simple typo or misplaced character in the URL can prevent the server from understanding your request.
What to do:

Pro-tip: Keep your website’s URLs simple and user-friendly to minimize the risk of typos.
If you still get a 400 Bad Request error after trying all these tips, continue to the following method.
2. Clear Your Browser’s Cache and Cookies
Your browser saves site data in a cache, so when you revisit the site in the future, the browser can serve the cached content to make the page load faster.
Cache
A cache is a temporary data storage layer that is designed to improve data access speeds by reducing the time needed to read and write data from a permanent data storage location.
Read More
As you’re browsing the Internet, cookies will also be stored in your browser. These are small files that contain data such as the length of your browsing session. Cookies can also remember personalized information like your login details or site preferences.
Although your browser’s cache and cookies can be helpful tools, they can also become corrupted, and cookies can eventually expire. When this happens, it can trigger a 400 Bad Request. To solve this problem, consider clearing the cache and cookies in your browser.
Why this helps: Over time, cache and cookies can become outdated or corrupted, leading to communication issues with the server.
What to do:
- In Google Chrome, click on the three-dot menu in the upper-right corner, select More Tools > Clear Browsing Data.
- In Mozilla Firefox, click on the three-line menu, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Cookies and Site Data > Clear Data.
- In Google Chrome, check Cookies and other site data.
- In Mozilla Firefox, check Cached images and files.
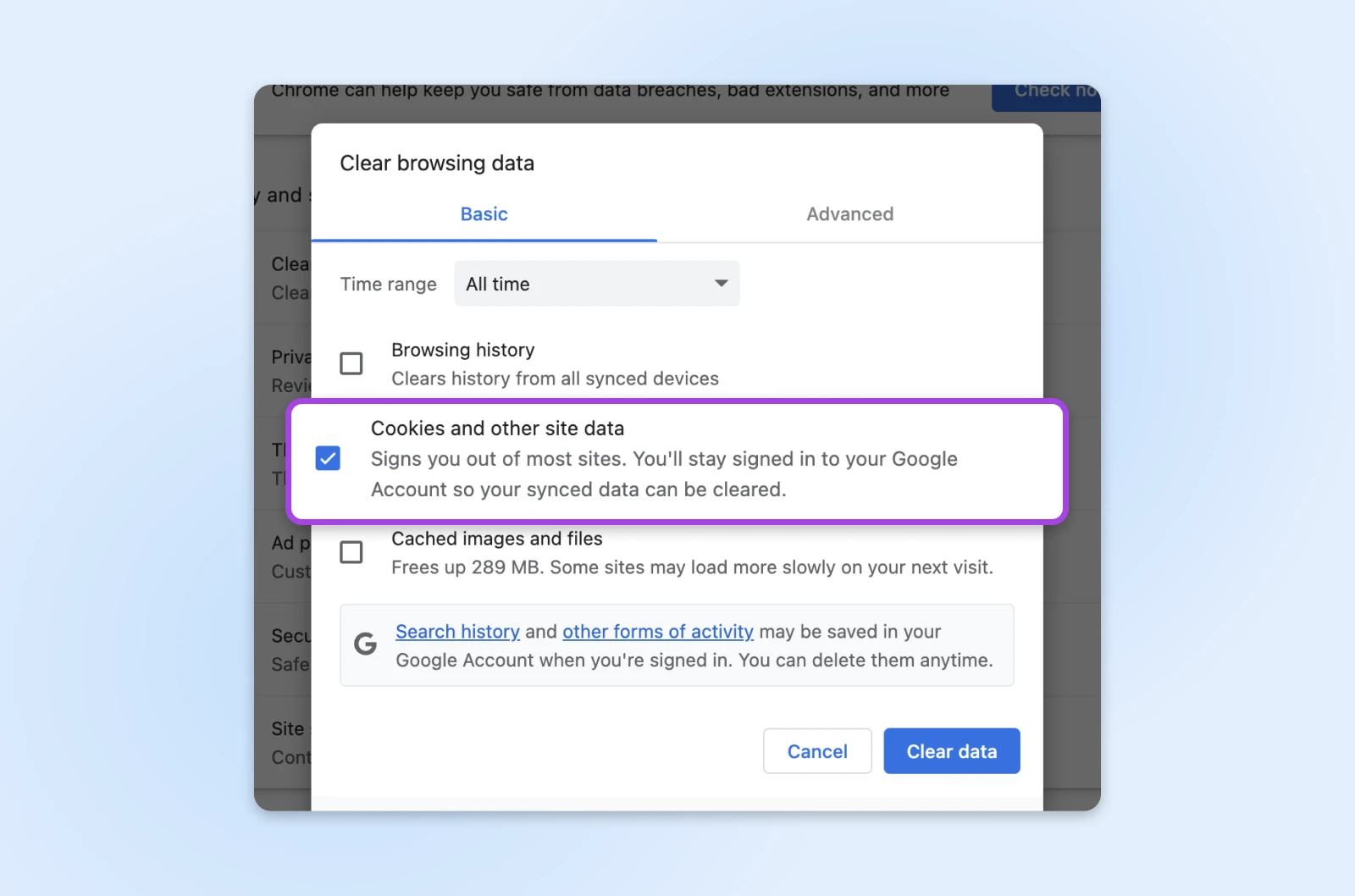

Keep in mind that this will sign you out of many websites. You may also experience slower loading times when you visit these sites again. However, it could remove corrupted or expired data that may cause a 400 Bad Request.
3. Disable Browser Extensions
If you’re a website owner, you likely know that third-party plugins can cause many WordPress errors. Similarly, the software in your browser extensions could interfere with your request, so try disabling extensions temporarily if you’re seeing 400 Bad Request errors.
Why this helps: Some extensions may interfere with website requests, especially those related to security or content filtering.
What to do:
- In Chrome, go to the three-dot menu > Extensions > Manage Extensions.
- In Firefox, click on the three-line menu > Add-ons and themes.
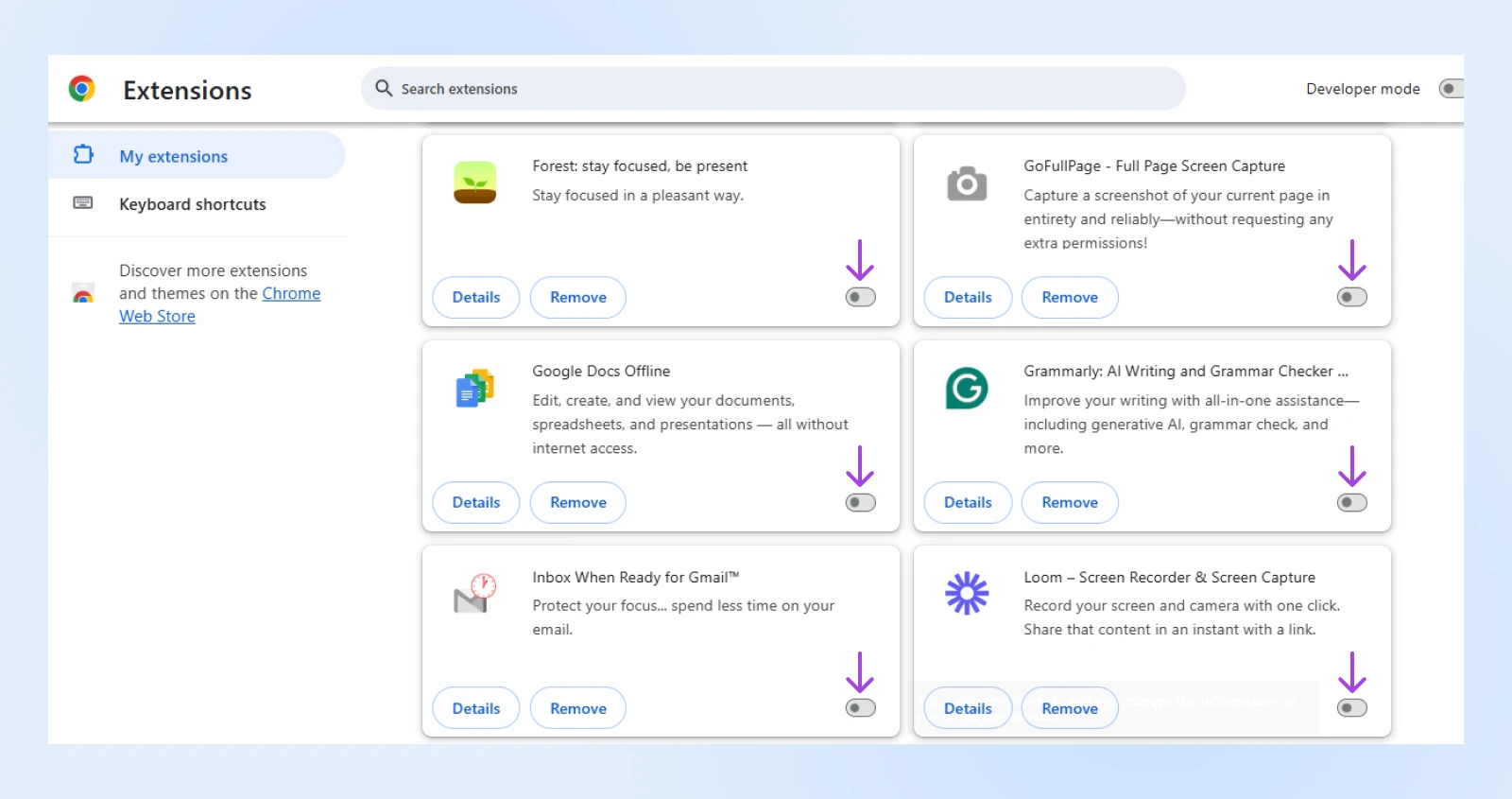

Some extensions are more likely to be common offenders than others when it comes to 400 Bad Request errors. These include: ad blockers, privacy extensions, or VPN-related add-ons.
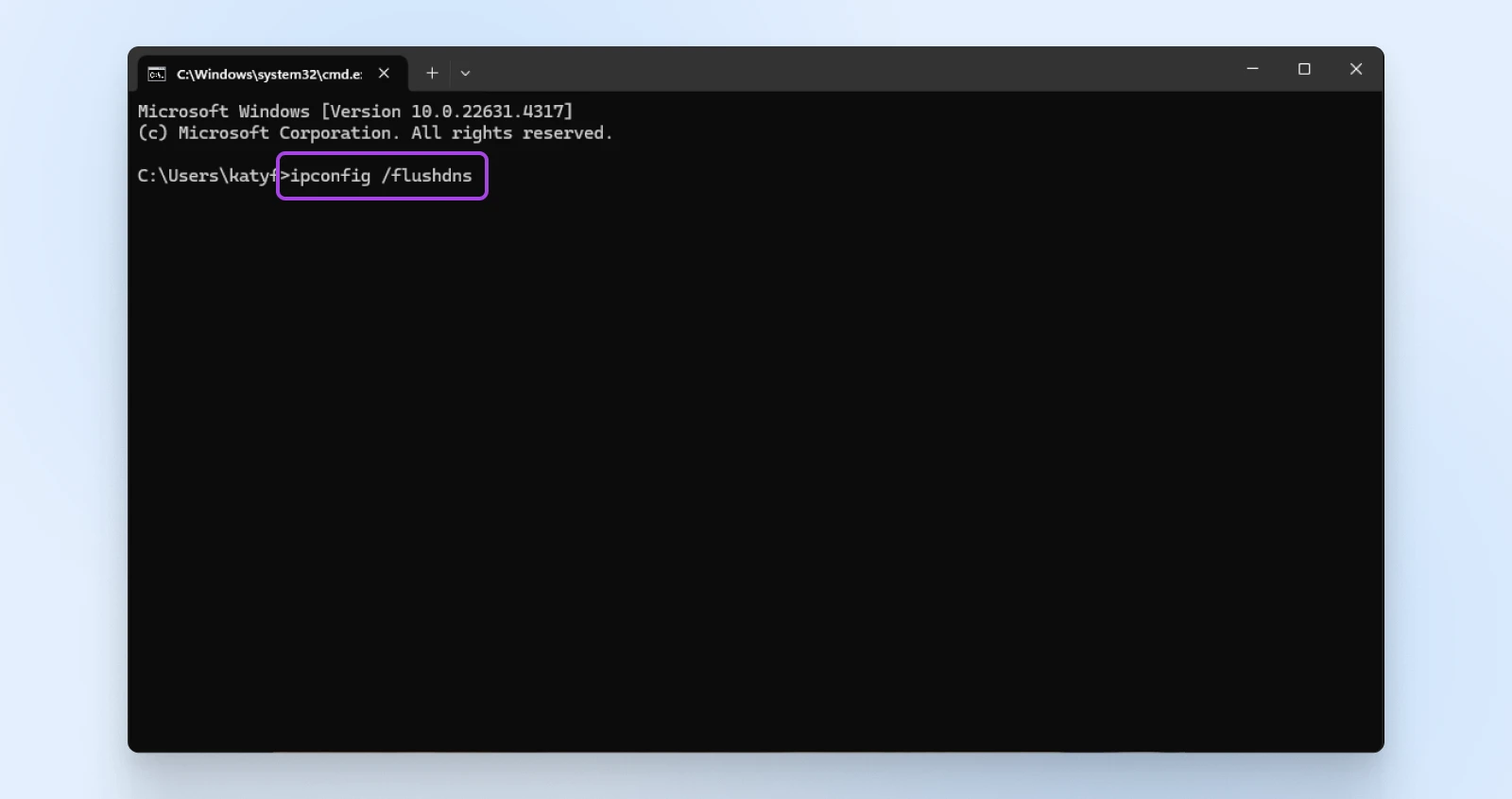
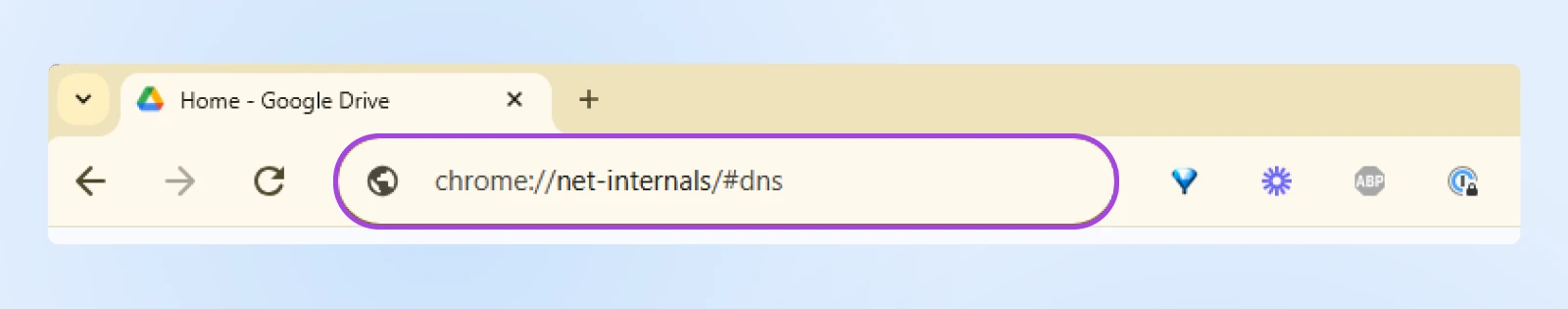
4. Flush the DNS Cache
The first time you visit a website, some of its data is stored locally in a cache. To load pages faster, your computer will save DNS information about websites. This will eliminate the need to search for the site’s nameserver and IP address every time you come back.
Just like your browser cache, the DNS cache can also become corrupt or outdated. Sometimes, a website will update its DNS information. If this conflicts with your cached data, it can lead to a 400 Bad Request error. To fix this error, you’ll need to flush your DNS cache.
Why this helps: Clearing the DNS cache ensures your computer communicates with the most recent DNS information.
What to do:
On Windows:

On Mac:
On Linux:
For browser DNS cache (Chrome):

After you successfully flush your DNS, check to see if this resolves the error. If not, you’ll need to try another method…
5. Check the Uploaded File Size
Sometimes, you’ll see the 400 Bad Request error right after uploading a file to a website. In this case, your file may be too big to upload to the site’s server.
To see if this is the case, start by uploading a smaller file. If this is successful, you’ll need to resize or compress the original file.
Why this helps: Uploading files larger than the server’s limit can trigger a 400 error. Every site has a maximum file upload size. Although this is set by the hosting provider, it usually falls between 2 MB and 500 MB. If you upload a larger file, you’ll likely receive a Bad Request.
What to do:
- For images: Use tools like TinyPNG to compress images and reduce file sizes without losing quality.
- For documents: Compress files into a ZIP folder.
6. Troubleshoot Your Device and Internet Connection
Now, if every single page you visit returns a 400 Bad Request, you might just have a poor internet connection. To see if this is the case, try switching to a different network. For example, you can turn off Wi-Fi for your mobile device and use cellular data.
Why this works: Network issues can prevent requests from reaching the server correctly.
If this resolves the error, you can troubleshoot your Internet connection.
What to do:
- On MacOS, use the Wireless Diagnostics tool.
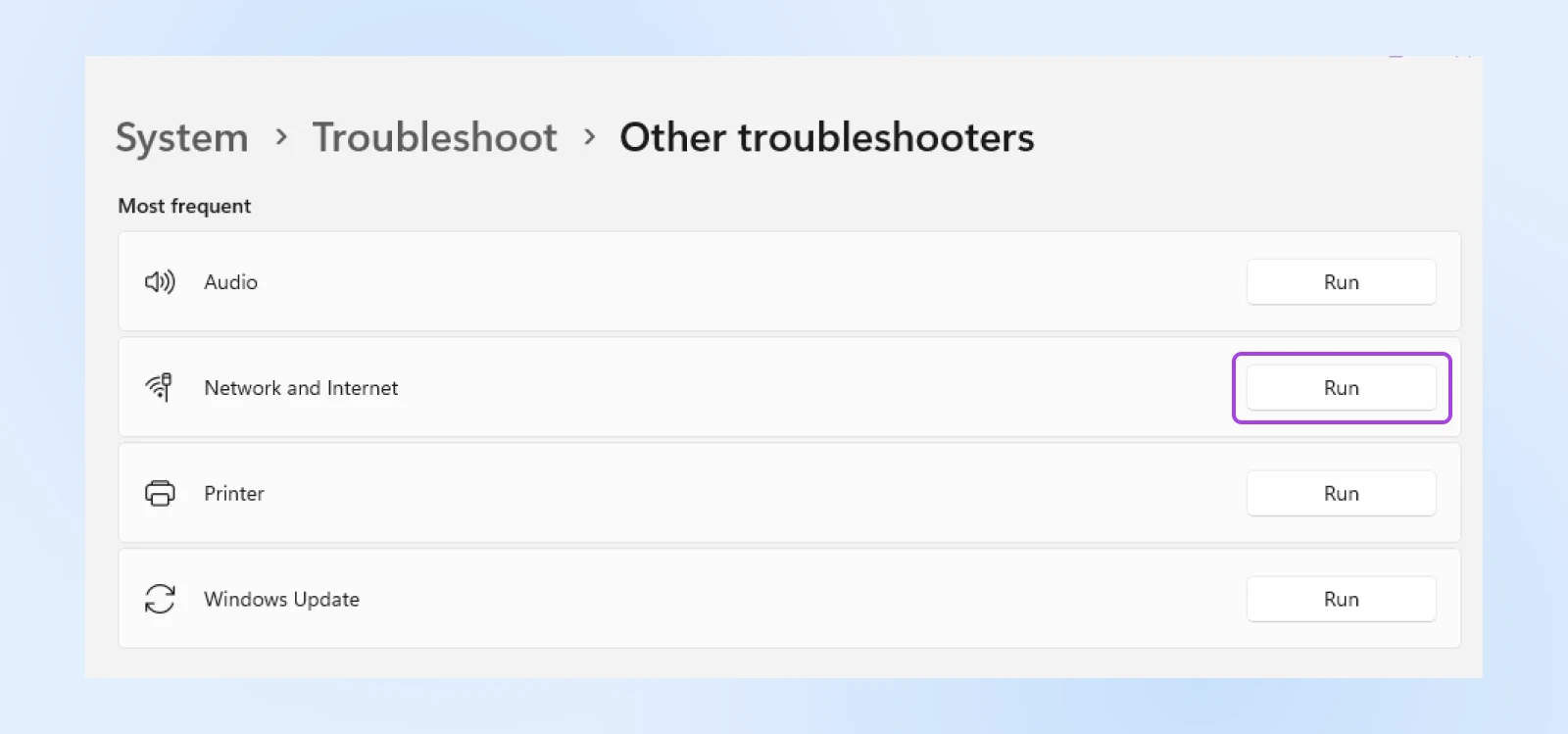
- On Windows 11, go to Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters > Network and Internet. Click Run.

If none of these options clear the error and you’re still getting a 400 Bad Request error on multiple or all websites, consider contacting your service provider to help fix the issue.
Monitoring and Preventing 400 Bad Request Errors
Being proactive can save you from future headaches. Here’s how to keep an eye on your website’s health:
Use Website Auditing Tools
Tools like Google Search Console can scan your website for errors, including 400 Bad Request issues. Here’s what to do:
Regularly Update Your Website
Keeping your website updated prevents critical security issues and other problems that can cause errors, including 400 errors. Keep all components, especially things like plugins and themes, up to date to ensure compatibility. And make sure your content management system (CMS) is always updated to the latest version.
Educate Your Team
Make sure anyone who adds content or manages your site is aware of best practices to avoid introducing errors —including everything we’ve covered so far in this article.
When To Seek Professional Assistance
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, the 400 Bad Request error persists. Then, it might be time to call in the experts.
Indicators that you might need help resolving a 400 Bad Request error:
- Server-side issues: If the error is due to server misconfigurations or database problems, it might be outside of your control.
- Widespread impact: If multiple users report the same error across different devices and networks, you might need professional assistance getting it solved quickly before the effects snowball.
- Lack of time and/or expertise: Business owners are busy, and your time is valuable. If you have too much on your plate and can’t focus on a website error right now, it’s better to ask a professional for help.
How DreamHost can help: At DreamHost, we’re committed to supporting you in maintaining a flawless online presence. Our award-winning, in-house support staff and service team are on hand 24/7 to help with whatever you need, including 400 Bad Request errors. Our experts can:
- Diagnose and fix server-side issues.
- Provide guidance on optimizing your website.
- Offer hosting solutions tailored to small businesses.
Get Ready for Error-Free Browsing
The 400 Bad Request error can be a stumbling block, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s one you can overcome. By understanding the causes and implementing these fixes, you’re taking proactive steps to ensure a seamless experience for your visitors — a critical factor in the success of your business.
Fortunately, there are many ways to resolve the issue. One simple solution is to reload the browser and check for temporary glitches. However, you may need to flush your DNS cache, restart your device, or reduce uploaded file sizes.
Remember, you don’t have to navigate these challenges alone. Stay ahead of potential issues by subscribing to the DreamHost Blog for more tips, or explore our range of services designed to empower small business owners like you.
Educate your team on other common website errors with these helpful guides:



